Introduction
Elabscience® Cell Stimulation and Protein Transport Inhibitor Kit is an optimized
broad-spectrum immune cell stimulator and inhibitor that can induce and
stimulate a variety of cells in vitro to produce cytokines and block the
transport of secreted proteins to the extracellular.
Cell stimulation and Protein Transport
Inhibitor Kit is mainly composed of Cell Stimulation MIX and Protein Transport
Inhibitor MIX. Cell Stimulation MIX is a mixture of Phorbol 12-Myristate 13-Acetate
(PMA) and Ionomycin, which can induce various cell activation and secrete
cytokines.
Protein Transport Inhibitor MIX is
mainly composed of Monensin and Brefeldin A, which can prevent the loss of
cytokine transport. After cell membrane rupture, cytokines can be detected.
Reagent Preparation
1) 500×Cell
Stimulation MIX
Add 100 μL Cell Stimulation MIX Solvent to dissolve a vial of Cell
Stimulation MIX and mix fully.
2) 1000×Protein
Transport Inhibitor MIX
Add 50 μL absolute ethanol (self-prepared) to a vial of Protein
Transport Inhibitor MIX and mix fully.
Note: Centrifuge at 2000~10000×g
for several seconds before use and then open the cover for use. Absolute
ethanol is volatile, please keep it sealed properly.
Experimental Procedure
Application 1: Cytokine content or activity detection in
cell culture supernatant
1. Prepare the single cell suspension with complete medium (self-prepared),
and adjust the cell density to 1~2×106/mL.
Note: The cell density should not be too high, and the
maximum density should be less than 2×106/mL, high cell density
will affect cell activation efficiency. Make sure the cells are in good
condition before stimulation, especially for freshly prepared primary cells.
2. Add 2 μL of 500× Cell Stimulation MIX to each 1 mL of
cell suspension, and incubate the cells at 37°C, 5%CO2 for 4~18 h (It is recommended
to determine the optimal induction time by setting up a pre-experiment with
different induction times for the cytokines to be tested. The common induction
time can be refer to table 1).
3. Collect cell culture supernatant for the subsequent detection or store at -80°C for later use (the supernatant contains
a variety of cytokines secreted by cells, which can be used to detect the
content and activity of cytokines by ELISA or other biochemical reagents).
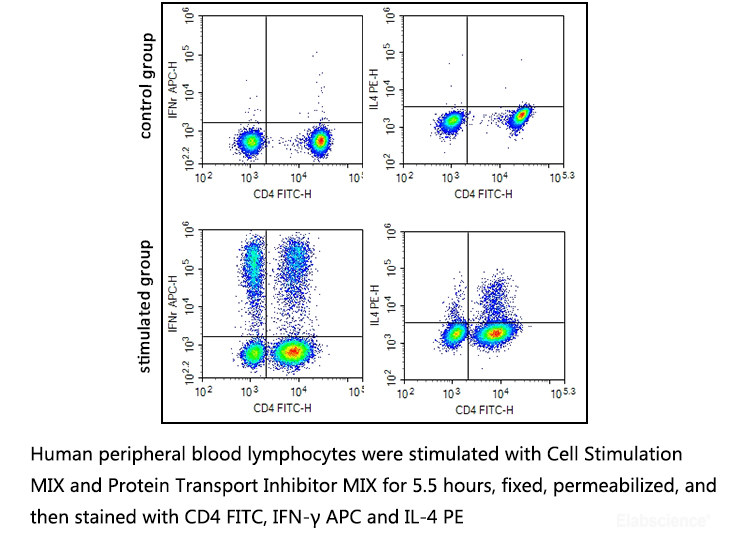
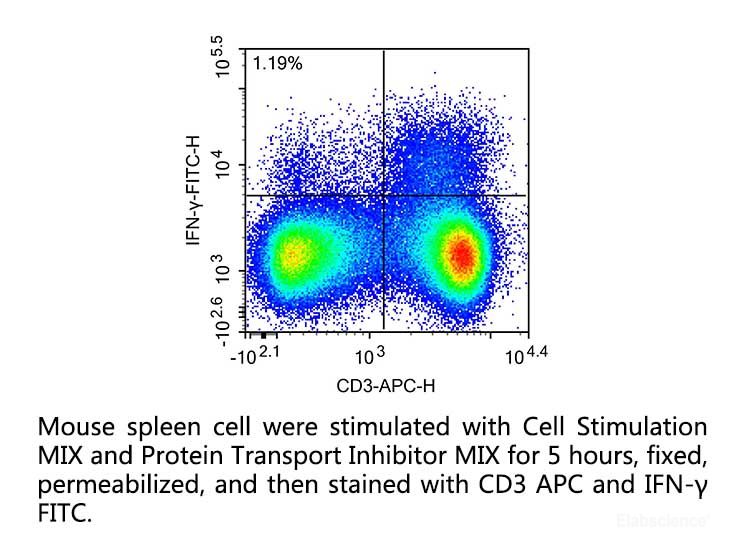
Application 2: Intracellular
factor detection
1. Prepare the single cell suspension with complete medium (self-prepared),
and adjust the cell density to 1~2×106/mL.
Note: The cell
density should not be too high, and the maximum density should be less than 2×106/mL,
high cell density will affect cell activation efficiency. Make sure the cells
are in good condition before stimulation, especially for freshly prepared
primary cells.
2. Add 2 μL of 500× Cell Stimulation MIX to each 1mL of cell
suspension, and incubate the cells at 37°C, 5%CO2 for 1.5~1 h.
3. Add 1 μL of 1000×Protein Transport Inhibitor MIX to each
1mL of cell suspension, and incubate the cells at 37°C, 5%CO2 for 5~16 h (It is recommended
to determine the optimal induction time by setting up a pre-experiment with
different induction times for the cytokines to be tested. The common induction
time can be refer to table 1).
4. Collect cell suspension, centrifuge at 200~300×g for 5 min, discard
the supernatant and collect the cell pellet which could be used for subsequent
intracellular factor detection after fixation.
Table 1: Reference of inducing condition of intracellular
factors
|
Species
|
Target cell
|
Cytokines/chemokines
|
Induction time
|
|
Mouse
|
Spleen T
lymphocytes
|
IL-17A
|
5~6 h
|
|
IFN-γ
|
5~6 h
|
|
IL-4
|
5~6 h
|
|
IL-2
|
5~6 h
|
|
IL-10
|
5~6 h
|
|
IL-6
|
5~6 h
|
|
Human
|
Peripheral blood T lymphocytes
|
IL-17A
|
5~6 h
|
|
IFN-γ
|
5~6 h
|
|
IL-4
|
5~6 h
|
|
IL-2
|
5~6 h
|
|
IL-6
|
5~6 h
|
|
IL-10
|
5~6 h
|
|
IL-21
|
5~6 h
|
Troubleshooting
|
Symptoms
|
Causes
|
Comments
|
|
No cytokines detected
|
The cell density is too large.
|
Adjust cell density to
1~2×106/mL.
|
|
Red blood cell interference.
|
Tissue containing more red blood cells should be
treated with red blood cell lysate first.
|
|
The reagent failed.
|
Preserve the reagent reasonably and use within the
validity period.
|
|
The antibody effect is not good.
|
Use effective antibody as positive control.
|
|
The effect of cell fixation and permeabilization is not
good.
|
Use effective fixative and permeabilization buffer.
|
|
The induction time is not enough.
|
Set the induction time gradient to select the best
induction time.
|
|
Overexpression of intracellular factors
|
Poor cell state and more dead cells.
|
Ensure that the cells are in good condition before
induction, and eliminate the interference of dead cells.
|
|
Non-specific binding of antibodies.
|
Increase antibody blocking process to reduce
non-specific binding.
|
|
Cytokines were detected in supernatants but not in
cells
|
The incubation time of 1000×Protein Transport Inhibitor
MIX is insufficient.
|
Appropriately increase the incubation time of
1000×Protein Transport Inhibitor MIX.
|
|
More cell loss
|
Centrifugal conditions are not appropriate.
|
Unfixed living cells centrifugal force is less than 300×g,
the speed of acceleration is less than 3,the speed of deceleration is less
than 2, which can greatly reduce the cell loss caused by centrifugation.
|
|
Too many cells, inadequate fixation.
|
Increase fixed liquid volume and extend fixation time.
|
Cautions
1. This kit is for research use only.
2. Due to the effect of Brefeldin A in Protein Transport Inhibitor MIX on CD69, it is recommended not to add Protein Transport Inhibitor MIX when detecting CD69. However, this operation may cause intracellular factors to be secreted outside the cell.
3. Please take safety precautions and
follow the procedures of laboratory reagent operation.
4. Please store the product at the
appropriate temperature to avoid failure.